Solar Panel Companies: An Essential Guide to Providers, Installers, and Industry Structure
The solar energy industry has experienced remarkable growth as homeowners and businesses seek sustainable energy solutions. Understanding the landscape of solar panel companies, installers, and the broader industry structure is essential for anyone considering a transition to renewable energy. This guide explores the key players, installation processes, and what distinguishes various providers in this evolving market.

The solar energy sector encompasses a diverse network of manufacturers, distributors, and installation professionals working together to deliver renewable energy solutions. Navigating this landscape requires understanding the different types of companies involved and how they contribute to bringing solar power to residential and commercial properties.
What Are Solar Panel Companies and Their Roles?
Solar panel companies operate across multiple segments of the industry. Manufacturers produce photovoltaic cells and panels, creating the core technology that converts sunlight into electricity. These companies invest heavily in research and development to improve efficiency and reduce production costs. Distribution companies bridge the gap between manufacturers and local markets, managing supply chains and ensuring panels reach regional installers. Some companies operate vertically, handling manufacturing, distribution, and installation under one brand, while others specialize in specific segments.
How Do Solar Installers Differ from Panel Manufacturers?
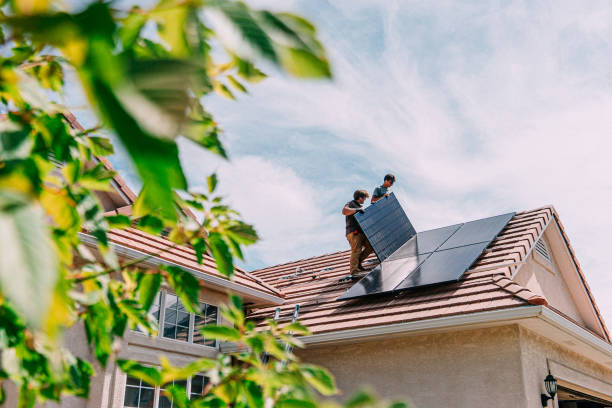
Solar installers are specialized contractors who design, permit, and install solar energy systems on residential and commercial properties. Unlike manufacturers who focus on producing panels, installers assess site conditions, calculate energy needs, recommend system sizes, and handle the physical installation process. They navigate local building codes, secure necessary permits, and ensure systems meet electrical safety standards. Many installers partner with multiple manufacturers, offering customers various panel options based on budget, efficiency requirements, and aesthetic preferences. The installer’s expertise significantly impacts system performance, as proper placement, angle optimization, and electrical integration are critical for maximizing energy production.
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Solar Installation Company?
Selecting a solar installation company requires evaluating several factors beyond price alone. Experience and track record matter significantly—companies with extensive installation histories typically navigate challenges more effectively. Certification and licensing demonstrate professional standards, with credentials from organizations like the North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners indicating qualified technicians. Warranty offerings vary considerably, covering equipment, workmanship, and performance guarantees for different durations. Customer reviews and references provide insight into communication quality, project timelines, and post-installation support. Financial stability is also important, as companies must remain operational to honor long-term warranties. Local knowledge proves valuable, as installers familiar with regional regulations, climate conditions, and utility interconnection requirements streamline the process.
Understanding the Solar Industry Structure and Market Dynamics
The solar industry operates through interconnected tiers. Tier 1 manufacturers are typically large, financially stable companies with automated production and extensive quality control. Tier 2 and 3 manufacturers may offer competitive pricing but with varying quality assurance levels. The installation sector includes national chains with standardized processes and local independent contractors offering personalized service. Financing companies have emerged as crucial players, providing loans, leases, and power purchase agreements that make solar accessible without large upfront investments. Utility companies increasingly participate through community solar programs and interconnection agreements. This complex ecosystem means consumers interact with multiple entities throughout the solar adoption process.
Real-World Cost Considerations and Provider Comparisons
Understanding the financial landscape helps set realistic expectations when exploring solar options. Installation costs vary based on system size, panel quality, roof complexity, and regional labor rates. Residential systems typically range from moderate to significant investments depending on energy needs and equipment choices. Different providers offer various financing structures, from direct purchases to lease agreements and power purchase arrangements.
| Provider Type | Services Offered | Cost Structure | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Installation Companies | Full-service installation, financing options, standardized warranties | Mid to high range pricing, various financing plans | Established processes, may subcontract local work |
| Local Independent Installers | Personalized design, direct installation, local expertise | Variable pricing, often competitive | Strong community ties, flexible customization |
| Manufacturer Direct Programs | End-to-end service from production to installation | Premium pricing with integrated warranties | Streamlined communication, single point of contact |
| Community Solar Programs | Subscription-based solar access without installation | Monthly subscription fees, no upfront costs | No equipment ownership, suitable for renters |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
System pricing depends on numerous variables including equipment quality, installation complexity, local incentives, and financing terms. Many regions offer tax credits, rebates, or performance-based incentives that significantly reduce net costs. Obtaining multiple quotes from different provider types allows comparison of equipment specifications, warranty terms, and total project costs.
How Technology and Innovation Shape Solar Companies
Technological advancement drives competition among solar companies. Panel efficiency has increased substantially, with modern panels converting higher percentages of sunlight into electricity within the same physical footprint. Inverter technology has evolved from string inverters to microinverters and power optimizers, improving system performance and monitoring capabilities. Battery storage integration has become increasingly common, allowing energy storage for nighttime use or backup power. Companies investing in these technologies often command premium pricing but deliver enhanced performance and flexibility. Software platforms for system monitoring, energy management, and predictive maintenance differentiate forward-thinking providers. As technology continues advancing, the gap between innovative companies and those using older methods widens.
Conclusion
The solar industry’s structure reflects a maturing market with diverse participants serving different customer needs. Understanding the distinction between manufacturers, installers, and service providers helps consumers make informed decisions aligned with their energy goals and financial situations. Whether prioritizing cutting-edge technology, local expertise, or comprehensive warranties, the expanding solar marketplace offers options for various preferences. Thorough research, multiple consultations, and careful comparison of proposals remain essential steps toward successful solar adoption.