Packing and Warehouse in the Netherlands – Precision, Structure and Everyday Efficiency
The Netherlands has established itself as a central hub for logistics and distribution across Europe. Its packing and warehouse operations are recognised for their structured approach, advanced infrastructure, and commitment to quality standards. From food processing to electronics assembly, facilities across the country handle millions of products daily with attention to detail and operational consistency. Understanding how these environments function offers insight into the broader logistics landscape that supports international trade and domestic supply chains.

The packing and warehouse sector in the Netherlands forms a vital component of the country’s economy. With its strategic location, well-developed transport networks, and strong trade relationships, the nation serves as a gateway for goods moving throughout Europe. Facilities range from small-scale distribution centres to large automated warehouses that process thousands of orders each day. These environments are designed to ensure that products reach their destinations safely and on time through systematic processes and quality control measures.
How are packing and warehouse processes structured in Dutch production and storage facilities?
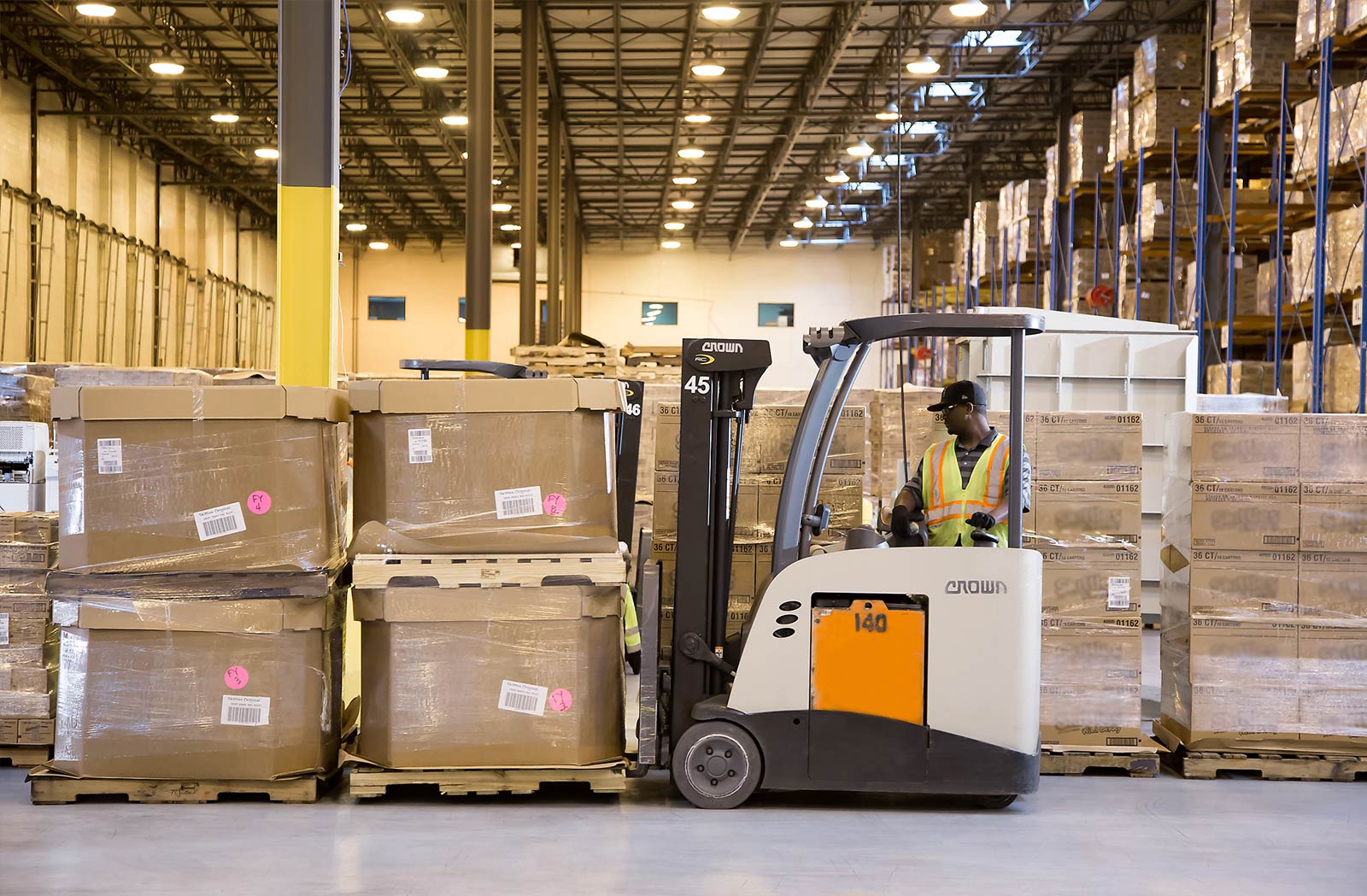
Packing and warehouse operations in the Netherlands follow clearly defined workflows designed to maximise efficiency and minimise error. Upon arrival, goods are received, inspected, and logged into inventory management systems. Items are then sorted and stored according to category, size, or destination. Packing stations are typically organised in assembly-line fashion, where products are prepared for shipment by wrapping, boxing, labelling, and sealing according to specific requirements. Quality checks occur at multiple stages to ensure compliance with client specifications and safety regulations. These processes reflect the systematic nature of modern logistics operations across the country.
What materials and systems support efficiency, precision, and safe handling of goods?
Modern Dutch warehouses rely on a combination of traditional materials and advanced technological systems. Packaging materials include corrugated cardboard, bubble wrap, shrink film, pallets, and protective foam, all selected based on the nature of the goods being handled. Barcode scanners and radio-frequency identification systems enable real-time tracking of inventory, reducing the likelihood of misplacement or loss. Conveyor belts, forklifts, and automated picking systems streamline the movement of goods within large facilities. Personal protective equipment such as gloves, safety shoes, and high-visibility vests are standard to ensure workplace safety. Ergonomic workstations and adjustable packing tables help reduce physical strain during repetitive tasks. Climate-controlled storage areas are used for temperature-sensitive products, while secure zones are designated for high-value items.
How does organisation and teamwork contribute to consistent quality in daily operations?
Organisation and clear communication are essential to maintaining quality and meeting deadlines in packing and warehouse environments. Supervisors coordinate tasks, assign responsibilities, and monitor progress throughout operational periods. Operations often involve collaboration among multiple personnel, particularly when handling heavy or fragile items. Regular briefings ensure everyone understands priorities and any changes to procedures. Feedback mechanisms allow for reporting of issues or suggestions for improvements, fostering a culture of continuous enhancement. Training programmes establish safety protocols, equipment operation standards, and quality benchmarks. This structured approach reduces errors, improves operational flow, and supports the smooth functioning of complex logistics operations throughout the Netherlands.
Which standards define the precision and sustainability of modern packing environments in the Netherlands?
Dutch packing and warehouse facilities operate under strict national and European regulations. Health and safety standards require regular risk assessments, proper ventilation, fire safety measures, and clear emergency procedures. Environmental regulations encourage waste reduction, recycling of packaging materials, and energy-efficient lighting and heating systems. Many companies pursue certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Sustainability initiatives include the use of biodegradable packaging, electric forklifts, and solar panels on warehouse rooftops. Labour laws ensure fair working conditions, including maximum working hours, rest breaks, and access to facilities. These standards reflect the Netherlands’ commitment to balancing economic productivity with social responsibility and environmental stewardship across its industrial sectors.
How is the packing and warehouse sector evolving with new technologies and industrial innovation?
The packing and warehouse sector in the Netherlands is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological innovation. Automation is increasingly common, with robotic arms performing repetitive tasks such as sorting, packing, and palletising. Warehouse management software integrates with enterprise resource planning systems to optimise inventory levels and predict demand patterns. Artificial intelligence algorithms analyse data to improve route planning for goods movement within facilities. Augmented reality devices assist in locating items quickly and accurately. Drones are being tested for inventory audits in large warehouses. These advancements demonstrate how the sector adapts to changing market demands while maintaining operational efficiency. The integration of new technologies continues to shape the logistics landscape across the Netherlands, influencing how facilities operate and manage resources.
The packing and warehouse sector in the Netherlands exemplifies how structure, precision, and systematic organisation support the smooth flow of goods across borders and industries. Facilities combine established practices with emerging technologies to meet the demands of a dynamic global market. As the sector evolves, it remains a cornerstone of the Dutch economy, reflecting broader trends in logistics, sustainability, and industrial innovation.