Call Center & Customer Communication in Sweden – Structure, Workflows and Modern Service Environments
Sweden's customer communication landscape has evolved into a sophisticated ecosystem where technology, efficiency, and employee wellbeing intersect. Contact centers across the country serve as vital touchpoints between organizations and their audiences, handling inquiries, resolving issues, and maintaining relationships. Understanding how these operations function, the skills they require, and the technologies they employ offers insight into a sector that continues to adapt to changing expectations and digital transformation.
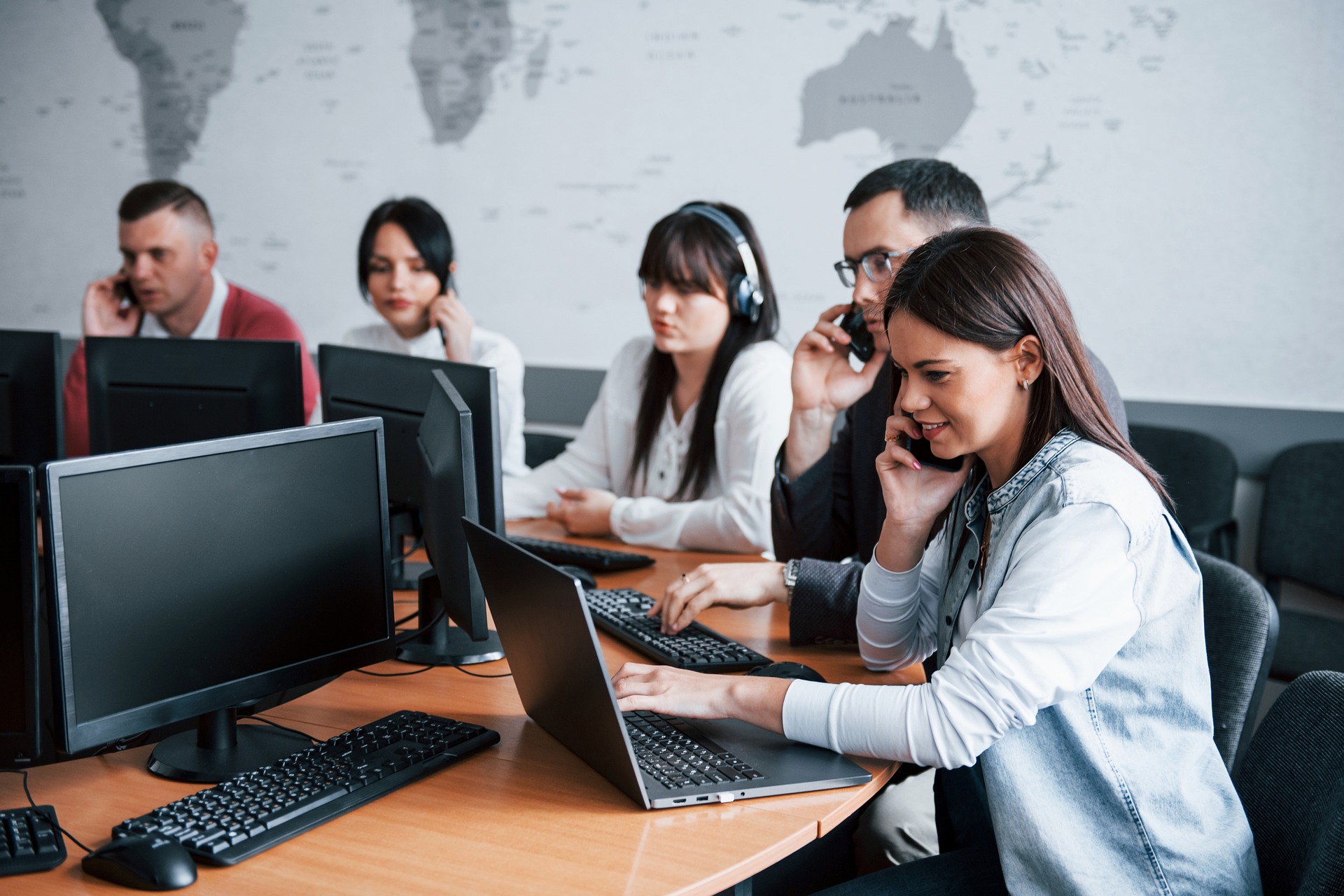

A Contemporary Approach to Customer Interaction
Swedish contact centers have embraced a balanced approach that prioritizes both customer satisfaction and employee experience. Unlike traditional models focused solely on call volume, modern facilities integrate multiple communication channels including phone, email, chat, and social media. This omnichannel strategy reflects consumer preferences for flexibility and immediate responses. Organizations recognize that quality interactions build loyalty and reduce long-term service costs. The Swedish emphasis on work-life balance and employee rights has also shaped how these environments operate, with attention to scheduling flexibility, manageable workloads, and continuous professional development. Cultural values around transparency and equality influence communication styles, encouraging agents to engage authentically rather than follow rigid scripts.
How Processes Are Organised in Swedish Contact Centers
Operational structure in Swedish contact centers typically follows a tiered system designed to route inquiries efficiently. First-level support handles common questions and straightforward requests, often using knowledge bases and standardized procedures. More complex issues escalate to specialized teams with deeper product or technical expertise. Workforce management tools forecast call volumes based on historical data, seasonal patterns, and marketing campaigns, allowing supervisors to schedule staff appropriately. Quality assurance processes involve regular call monitoring, feedback sessions, and performance metrics that balance speed with resolution quality. Many facilities implement continuous improvement methodologies, gathering agent input on process bottlenecks and customer pain points. Collaboration between departments ensures that feedback from customer interactions informs product development and policy adjustments.
Daily Operations in Modern Swedish Call Centers
A typical workday in a Swedish contact center begins with team briefings where supervisors share updates on system changes, new products, or emerging issues. Agents log into integrated platforms that consolidate customer information, communication history, and support resources. Throughout their shifts, they navigate between inbound calls, responding to digital messages, and updating customer records. Break schedules are carefully managed to maintain service levels while respecting labor regulations that protect employee wellbeing. Real-time dashboards display queue lengths and wait times, helping teams adjust their pace during unexpected volume spikes. After-call work involves documenting interactions, categorizing issues, and sometimes following up via email. Regular coaching sessions provide opportunities to review challenging calls and develop communication techniques. The environment balances productivity expectations with support systems designed to prevent burnout.
Skills Important in Swedish Customer Communication
Effective customer communication in Sweden requires a blend of technical competence and interpersonal abilities. Language proficiency stands as a foundational requirement, with many positions demanding fluency in Swedish and English, and sometimes additional Nordic or European languages. Active listening skills enable agents to understand underlying concerns beyond the stated problem. Problem-solving abilities help navigate situations where standard procedures do not apply, requiring creative solutions within policy boundaries. Emotional intelligence allows representatives to manage frustrated customers while maintaining composure and empathy. Technical aptitude is increasingly important as agents work with multiple software systems simultaneously, from CRM platforms to specialized troubleshooting tools. Adaptability helps staff adjust to frequent system updates, policy changes, and evolving customer expectations. Written communication skills matter as much as verbal ones, given the volume of email and chat interactions. Cultural awareness supports interactions with diverse customer bases and international colleagues.
Technology as a Central Component in Sweden
Swedish contact centers leverage advanced technology to enhance both efficiency and service quality. Cloud-based platforms enable remote work arrangements that became standard during recent years, allowing organizations to access broader talent pools while offering employees geographic flexibility. Artificial intelligence assists through chatbots that handle routine inquiries, freeing human agents for complex issues requiring judgment and empathy. Predictive analytics help forecast demand patterns, optimizing staffing levels and reducing wait times. Integrated CRM systems provide agents with comprehensive customer histories, enabling personalized interactions and reducing repetitive information requests. Speech analytics tools analyze call recordings to identify training opportunities and emerging trends. Workforce management software balances service level targets with employee preferences for shifts and time off. Quality monitoring systems randomly select interactions for review, ensuring consistency and identifying coaching opportunities. Collaboration tools facilitate knowledge sharing among teams and enable quick escalation when specialized expertise is needed. Security protocols protect sensitive customer data while maintaining compliance with European privacy regulations.
The Evolving Landscape of Customer Service in Sweden
The customer service sector in Sweden continues to transform as digital expectations rise and automation capabilities expand. Organizations invest in training programs that develop both technical skills and emotional intelligence, recognizing that human interaction remains valuable for complex or sensitive situations. Hybrid models combine self-service options for straightforward tasks with human support for nuanced problems. Remote work has become a permanent feature for many operations, requiring new approaches to team cohesion and performance management. Sustainability considerations influence facility design and operational practices, reflecting broader Swedish environmental commitments. Career pathways within contact centers have expanded, offering progression into specialized roles, team leadership, or adjacent functions like training and quality assurance. The sector faces ongoing challenges around recruitment and retention, prompting employers to enhance compensation, benefits, and workplace culture. As customer expectations continue evolving, Swedish contact centers adapt by balancing technological innovation with the human touch that builds lasting relationships and trust.