A Complete Guide to Scissor Lifts: How They Work and What They're Used For
Scissor lifts are essential pieces of equipment in construction, warehousing, and maintenance industries, providing safe and efficient access to elevated work areas. These hydraulic or electric-powered platforms use a crisscrossing metal framework that extends and retracts vertically, offering stable support for workers and materials at various heights. From compact indoor models to heavy-duty outdoor units, scissor lifts have revolutionised how professionals approach elevated tasks, significantly improving workplace safety whilst reducing project completion times across multiple sectors.
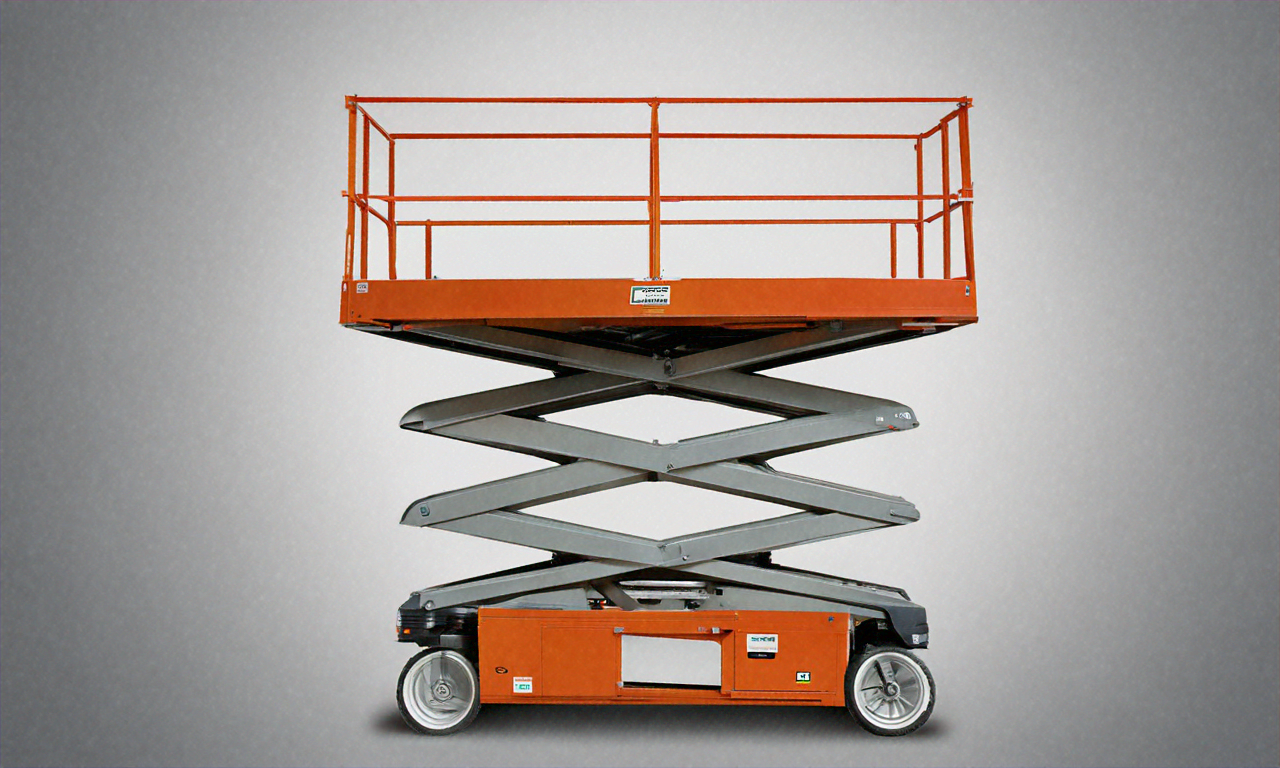

Scissor lifts have become indispensable tools across numerous industries, transforming the way professionals approach elevated work tasks. These versatile machines combine safety, efficiency, and precision to provide reliable access to heights that would otherwise require ladders, scaffolding, or other less stable alternatives.
Understanding Scissor Lifts
A scissor lift operates on a relatively straightforward mechanical principle that delivers impressive results. The equipment features a platform supported by a series of linked, folding supports arranged in a crisscross pattern resembling scissors. This distinctive design gives the machinery its name and enables smooth vertical movement. The scissor mechanism is powered by hydraulic cylinders, electric motors, or pneumatic systems that extend and retract the supporting framework, raising or lowering the platform in a controlled manner.
The platform itself typically includes safety railings, control panels, and emergency stop mechanisms. Most modern units incorporate multiple safety features such as tilt sensors, overload protection, and emergency lowering systems. The base of the scissor lift houses the power source, whether it be batteries for electric models or engines for diesel-powered variants, along with the control systems that manage the lifting mechanism.
How Scissor Lifts Operate
The operation of scissor lifts involves several interconnected systems working in harmony. When the operator activates the controls, the power source drives hydraulic pumps or electric motors that extend the scissor arms. As these arms unfold, they push the platform upward in a stable, vertical motion. The scissor design ensures that the platform remains level throughout the lifting process, providing a secure working surface at any height within the machine’s range.
Control systems vary depending on the model, but most feature both platform-mounted and ground-level controls. Platform controls allow operators to make fine adjustments whilst working at height, whilst ground controls enable positioning before personnel board the lift. Safety interlocks prevent operation when certain conditions are not met, such as when the platform is overloaded or when the machine is on unstable ground.
The descent process reverses the lifting operation, with hydraulic fluid returning to reservoirs or electric motors operating in reverse. Emergency descent systems provide backup lowering capabilities in case of power failure, ensuring operators can safely return to ground level under any circumstances.
Primary Scissor Lift Types
Scissor lifts come in various configurations designed to meet specific operational requirements. Electric scissor lifts are popular for indoor applications due to their quiet operation and zero emissions. These units typically feature compact designs, smooth operation, and precise positioning capabilities, making them ideal for retail environments, offices, and manufacturing facilities with height restrictions.
Diesel-powered scissor lifts offer greater power and higher lifting capacities, making them suitable for outdoor construction sites and heavy-duty applications. These robust machines can handle rough terrain and adverse weather conditions whilst providing extended operational periods without requiring battery charging or electrical connections.
Rough terrain scissor lifts represent a specialised category designed for challenging outdoor environments. These units feature enhanced traction systems, reinforced components, and increased ground clearance to navigate uneven surfaces, muddy conditions, and construction site obstacles effectively.
Stationary Scissor Lift Tables
Stationary scissor lift tables serve different purposes compared to their mobile counterparts. These fixed installations are commonly found in warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and loading docks where consistent vertical movement of materials is required. Unlike mobile units, stationary tables focus on load handling rather than personnel transport, though many can accommodate both functions.
These systems often integrate with existing facility infrastructure, including conveyor systems, automated storage solutions, and production lines. Installation typically involves permanent mounting to concrete foundations, with electrical and hydraulic connections routed through facility systems. Stationary tables can handle significantly heavier loads than mobile units, with some capable of lifting several tonnes.
Control systems for stationary installations frequently include remote operation capabilities, programmable positioning, and integration with facility management systems. This automation enables efficient material handling workflows and reduces manual labour requirements in industrial settings.
Mobile Scissor Lifts and Their Uses
Mobile scissor lifts provide exceptional versatility for applications requiring repositioning between work areas. These self-propelled units feature drive systems that allow operators to move the equipment whilst the platform is in lowered position, significantly improving productivity on large job sites.
Construction applications represent the largest market for mobile scissor lifts, where they facilitate electrical installation, painting, window installation, and general maintenance tasks. The ability to quickly relocate between work areas makes these machines particularly valuable for projects involving multiple buildings or extensive facilities.
Warehouse and retail environments also benefit significantly from mobile scissor lifts. These applications typically involve inventory management, facility maintenance, and seasonal decoration installation. The compact design of many mobile units allows operation in narrow aisles and confined spaces where larger equipment cannot access.
| Equipment Type | Typical Height Range | Load Capacity | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Scissor Lift | 6-40 feet | 500-1,500 lbs | Indoor maintenance, retail, offices |
| Diesel Scissor Lift | 20-60 feet | 1,000-2,500 lbs | Construction, outdoor projects |
| Rough Terrain Lift | 25-50 feet | 1,200-2,000 lbs | Construction sites, uneven surfaces |
| Stationary Table | 3-30 feet | 2,000-10,000 lbs | Warehouses, manufacturing |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The selection of appropriate scissor lift equipment depends on numerous factors including working height requirements, load capacity needs, environmental conditions, and operational frequency. Understanding these variables ensures optimal equipment selection and safe, efficient project completion. Modern scissor lifts continue evolving with technological advances, incorporating improved safety systems, enhanced efficiency, and greater operational capabilities to meet the demanding requirements of contemporary industrial applications.